L Designations
—See packings for high-pressure liquid chromatography in the
Chromatographic Reagents section under
Chromatography  621
621
.
Lactose,

C
12H
22O
11·H
2O—
342.30—Use ACS reagent grade.
Alpha Lactose Monohydrate
(
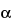
-
D-Lactose Monohydrate),

C
12H
22O
11·H
2O—
360.31—White powder. The
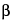
-
D-lactose content is less than 3%.
Assay—
Inject an appropriate derivatized specimen into a gas chromatograph (see
Chromatography  621
621
) equipped with a flame-ionization detector, helium being used as the carrier gas. The following conditions have been found suitable: a 0.25-mm × 30-m capillary column coated with a 1-µm layer of phase G2; the injection port temperature is maintained at 250

; the detector temperature is maintained at 280

; the column temperature is maintained at 230

and programmed to rise 4

per minute to 280

. The area of the C
12H
22O
11·H
2O peak is not less than 97% of the total peak area.
Beta Lactose
(
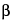
-
D-
Lactose),

C
12H
22O
11—
342.30—White to faint yellow powder. The
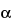
-
D-lactose content is not more than 35%.
Assay—
Inject an appropriate derivatized specimen into a gas chromatograph (see
Chromatography  621
621
) equipped with a flame-ionization detector, helium being used as the carrier gas. The following conditions have been found suitable: a 0.25-mm × 30-m capillary column coated with a 1-µm layer of phase G43; the injection port temperature is maintained at 250

; the detector temperature is maintained at 250

; the column temperature is maintained at 20

and programmed to rise 8

per minute to 280

. The area of the C
12H
22O
11 peak is not less than 99% of the total peak area.
Lanthanum Alizarin Complexan Mixture
—Use a suitable grade.
Lanthanum Chloride,

LaCl
3·(6–7)H
2O—This reagent is available in degrees of hydration ranging from 6 to 7 molecules of water. Use ACS reagent grade.
Lanthanum Oxide,

La
2O
3—
325.82


[
1312-81-8]—An almost white, amorphous powder, practically insoluble in water. It dissolves in dilute solutions of mineral acids and absorbs atmospheric carbon dioxide. Use Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy grade.
Lauryl Dimethyl Amine Oxide
 (N,N-Dimethyldodecylamine-N-oxide),
(N,N-Dimethyldodecylamine-N-oxide), C
14H
31NO



[
1643-20-5]—
229.41—Use a suitable grade.
Lead Acetate,

Pb(C
2H
3O
2)
2·3H
2O—
379.33—Use ACS reagent grade.
Lead Acetate Paper—
Immerse filter paper weighing about 80 g per square meter in a mixture of diluted acetic acid and lead acetate TS (1:10). Remove, dry, and cut into 15-mm × 40-mm strips.
Lead Monoxide
(
Litharge),

PbO—
223.20—Heavy, yellowish or reddish-yellow powder. Insoluble in water and in alcohol; soluble in acetic acid, in diluted nitric acid, and in warm solutions of the fixed alkali hydroxides.
Assay—
Accurately weigh about 300 mg, freshly ignited in a muffle furnace at 600 ± 50

, and dissolve it by warming with 10 mL of water and 1 mL of glacial acetic acid. Dilute with 75 mL of water, heat to boiling, add 50.0 mL of 0.1 N potassium dichromate VS, and boil for 2 to 3 minutes. Cool, transfer to a 200-mL volumetric flask with the aid of water, dilute with water to volume, mix, and allow to settle. Withdraw 100.0 mL of the clear liquid, and transfer to a glass-stoppered flask. Add 10 mL of diluted sulfuric acid and 1 g of potassium iodide, insert the stopper, mix gently, and allow to stand for 10 minutes. Then titrate the liberated iodine, representing the excess of dichromate, with 0.1 N sodium thiosulfate VS, adding 3 mL of
starch TS as the endpoint is approached: each mL of 0.1 N potassium dichromate is equivalent to 7.440 mg of PbO. Not less than 98% is found.
Insoluble in acetic acid—
Dissolve 2 g in 30 mL of dilute glacial acetic acid (1 in 2), boil gently for 5 minutes, filter, wash the residue with diluted acetic acid, and dry at 105

for 2 hours: the residue weighs not more than 10 mg (0.5%).
Substances not precipitated by hydrogen sulfide—
Completely precipitate the lead from the filtrate obtained in the test for
Insoluble in acetic acid by passing hydrogen sulfide into it, filter, and wash the precipitate with 20 mL of water. To one-half of the mixed filtrate and washings add 5 drops of sulfuric acid, evaporate to dryness, and ignite at 800 ± 25

for 15 minutes: the residue weighs not more than 5 mg (0.5%).
Volatile substances—
Accurately weigh about 5 g, and heat strongly in a covered porcelain crucible: it loses not more than 2.0% of its weight.
Lead Nitrate,

Pb(NO
3)
2—
331.21—Use ACS reagent grade.
Lead Perchlorate,

Pb(ClO
4)
2·3H
2O—
460.15—Use ACS reagent grade.
Lead Tetraacetate,

C
8H
12O
8Pb—
443.38


[
546-67-8]—Colorless to pinkish crystals. Soluble in hot glacial acetic acid, in chloroform, in nitrobenzene, and in tetrachloroethane. Hydrolyzed by water, producing brown lead dioxide and acetic acid. Unstable in air.
Linalool
(3,
7-Dimethyl-1,
6-octadien-3-ol),

C
10H
18O—
154.25


[
78-70-6]—Use a suitable grade.
Linoleic Acid,

C
18H
32O
2—
280.4


[
60-33-3]—Clear, colorless liquid. Use a suitable grade.
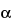 -Lipoic Acid,
-Lipoic Acid,

C
8H
14O
2S
2—
206.3


[
1077-28-7]—Yellow powder. Use a suitable grade.
Liquid Petrolatum
—Use Mineral Oil.
Lithium Chloride,

LiCl—
42.39—Use ACS reagent grade.
Lithium Hydroxide,

LiOH·H
2O—
41.96—Use ACS reagent grade.
Lithium Metaborate,

LiBO
2—
49.75—Use ACS reagent grade.
Lithium Nitrate,

LiNO
3—
68.95—Colorless crystals. Use a suitable grade labeled to contain not less than 97.0%.
Lithium Perchlorate,

LiClO
4—
106.39—Use ACS reagent grade.
Lithium Sulfate,

Li
2SO
4·H
2O—
127.96—Use ACS reagent grade.
Lithocholic Acid,

C
24H
40O
3—
376.57—White powder.
Assay—
When tested by thin-layer chromatography, with the use of plates coated with chromatographic silica gel mixture, a developing system consisting of a mixture of toluene, 1,4-dioxane, and acetic acid (15.2:4.2:0.6), and sprayed with a mixture of sulfuric acid and methanol (1:1), heated at 110

for 20 minutes, and examined visually and under long-wavelength UV light, a single spot is exhibited.
Litmus
—A blue pigment prepared from various species of
Rocella DeCandolle,
Lecanora Acharius, or other lichens (Fam. Parmeliaceae).
Description—
Cubes, masses, fragments, or granules, of an indigo blue or deep violet color. Has the combined odor of indigo and violets, and tinges the saliva a deep blue. The indicator substances it contains are soluble in water and less soluble or insoluble in alcohol.
Ash—
It yields not more than 60.0% of ash.
Locust Bean Gum
—A gum obtained from the ground endosperms of Ceratonia siliqua Linné Taub. (Fam. Leguminosae). Use Locust Bean Gum, FCC.
L-Lysine
(
2,
6-Diaminohexanoic Acid),

C
6H
14N
2O
2—
146.19—Crystalline needles or hexagonal plates. Soluble in water; very slightly soluble in alcohol; insoluble in ether.
Test solution:

20 mg per mL, in dilute hydrochloric acid (1 in 2).
Nitrogen content, Method I  461
461 :
:

between 18.88% and 19.44% of N is found, corresponding to not less than 98.5% of C
6H
14N
2O
2, the test specimen previously having been dried at 105

for 2 hours.