8-Azabicyclo[3.2.1]octane-2-carboxylic acid, 3-(benzoyloxy)-8-methyl-, methyl ester, [1R-(exo,exo)]-.
Methyl 3
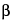
-hydroxy-1
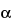 H
H,5
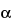 H
H-tropane-2
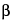
-carboxylate benzoate (ester)



[
50-36-2].
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in well-closed, light-resistant containers.
Identification—
A:
Ultraviolet Absorption  197U
197U
—
Solution:
15 µg per mL.
Medium:
dilute hydrochloric acid (1 in 120).
Absorptivities at 233 nm, calculated on the dried basis, do not differ by more than 3.0%.
C:
Dissolve about 100 mg in a mixture of 0.4 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid (1 in 12) and water to make 5 mL, and add 5 drops of chromium trioxide solution (1 in 20): a yellow precipitate is formed, and it quickly redissolves when the mixture is shaken. Add 1 mL of hydrochloric acid: a permanent, orange-colored, crystalline precipitate is formed.
D:
Dissolve about 10 mg in 1 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid (1 in 600), and evaporate on a steam bath just to dryness. Dissolve the residue in 2 drops of water, and add 1 mL of potassium permanganate solution (1 in 300): a violet, crystalline precipitate is formed, and it appears brownish violet when collected on a filter, and shows characteristic violet-red crystalline aggregates under the low power of a microscope, similar to those obtained from
USP Cocaine Hydrochloride RS.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
—
Dry it over phosphorus pentoxide for 3 hours: it loses not more than 1.0% of its weight.
Limit of cinnamyl-cocaine and other reducing substances—
Dissolve about 300 mg of finely powdered Cocaine in 1 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid (1 in 12) with the aid of heat, if necessary, and dilute with water to 15 mL. Mix 5 mL of this solution with 0.3 mL of dilute sulfuric acid (1 in 35) and 0.1 mL of potassium permanganate solution (1 in 300): the violet color does not disappear entirely within 30 minutes.
Limit of isoatropyl-cocaine—
Dilute in a beaker 5 mL of the solution of Cocaine prepared in the test for
Cinnamyl-cocaine and other reducing substances with 80 mL of water, add 0.2 mL of 6 N ammonium hydroxide, and stir the solution vigorously for 5 minutes, occasionally rubbing the inner wall of the beaker with a stirring rod: a crystalline precipitate of cocaine is formed, and the supernatant is clear.
Assay—
Dissolve about 600 mg of Cocaine, previously dried and accurately weighed, in 50 mL of glacial acetic acid, add 1 drop of
crystal violet TS, and titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS to a green endpoint. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 30.34 mg of C
17H
21NO
4.