Color of solution  631
631 —
—
Matching solutions—
Prepare three solutions, A, B, and C, containing, respectively, the following parts of cobaltous chloride CS, ferric chloride CS, cupric sulfate CS, and dilute hydrochloric acid (1 in 40):
A—
3.0:3.0:2.4:31.6
B—
1.0:2.4:0.4:36.2
C—
0.6:2.4:0:37.0
Procedure—
Prepare a test solution by dissolving 100 mg of Bromocriptine Mesylate in 10.0 mL of methanol, and compare this solution with 10-mL portions of the Matching solutions in suitable matched tubes: the solution is clear and not darker in color than Matching solutions A, B, and C.
Loss on drying (see Thermal Analysis  891
891 )—
)—
Determine the percentage of volatile substances by thermogravimetric analysis on an appropriately calibrated instrument, using about 10 mg of Bromocriptine Mesylate, accurately weighed. Heat the specimen under test at the rate of 10

per minute in an atmosphere of nitrogen at a flow rate of about 45 mL per minute. Record the thermogram from ambient temperature to 160

: it loses not more than 4.0% of its weight.
Chromatographic purity—
Citrate buffer—
Prepare a 0.1 N citric acid solution, adjust with hydrochloric acid to a pH of 2.0, and mix.
Diluting solution—
Prepare a mixture of methanol and Citrate buffer (1:1).
Solution A—
Mix 57 mL of 0.01 M phosphate buffer having a pH of 7.0 and 43 mL of acetonitrile.
Solution B—
Mix 40 mL of 0.01 M phosphate buffer having a pH of 7.0 and 60 mL of acetonitrile.
Mobile phase—
Use variable mixtures of
Solution A and
Solution B as directed for
Chromatographic system. Make adjustments if necessary (see
System Suitability under
Chromatography  621
621
).
System suitability solution—
Dissolve accurately weighed quantities of
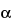
-ergocryptine and Bromocriptine Mesylate in
Diluting solution to obtain a solution containing about 2.0 mg of each per mL.
Standard solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of
USP Bromocriptine Mesylate RS in methanol, dilute quantitatively with an equal volume of
Citrate buffer, and dilute quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with
Diluting solution to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 4.6 µg per mL.
Test solution—
Transfer about 46 mg of Bromocriptine Mesylate, accurately weighed, to a 10-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in 5.0 mL of methanol, dilute with Citrate buffer to volume, and mix.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 300-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 15-cm column that contains 3-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 2 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
Time
(minutes) |
Solution A
(%) |
Solution B
(%) |
Elution |
| 0 |
100 |
0 |
equilibration |
| 0–18 |
100 |
0 |
isocratic |
| 18–30 |
100®0 |
0®100 |
linear gradient |
| 30–40 |
0 |
100 |
isocratic |
| 40–41 |
0®100 |
100®0 |
linear gradient |
Chromatograph the
System suitability solution, and record the peak responses as directed for
Procedure: the relative retention times are about 0.46 for
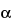
-ergocryptine and 1.0 for bromocriptine mesylate; the resolution,
R, between
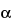
-ergocryptine and bromocriptine mesylate is not less than 15; and the tailing factor is not more than 1.5. Chromatograph the
Standard solution, and record the peak responses as directed for
Procedure: the retention time for the bromocriptine mesylate peak is between 17 and 20 minutes; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 10.0%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the
Standard solution and the
Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure all of the peak responses. Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Bromocriptine Mesylate taken by the formula:
1000F(C/W)(ri / rS),
in which
F, the relative response factor, is equal to 0.7 for any peaks eluting at a relative retention time of about 0.9 or less, and is equal to 1.0 for all other peaks;
C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of
USP Bromocriptine Mesylate RS in the
Standard solution; W is the weight, in mg, of Bromocriptine Mesylate taken for the
Test solution; ri is the peak response for each impurity obtained from the
Test solution; and
rS is the peak response for bromocriptine obtained from the
Standard solution: not more than 0.1% of any individual impurity is found; and not more than 0.5% of total impurities is found.