Loss on drying  731
731 —
—
Dry it in vacuum, but at a pressure not below 10 mm of mercury, at 60

to constant weight: it loses not more than 0.5% of its weight.
Chromatographic purity—
Solution A, Solution B, and Mobile phase —
Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Chromatographic system—
Proceed as directed in the Assay. To evaluate the system suitability requirements, use the Resolution solution and the Standard preparation prepared as directed in the Assay.
Test solution—
Dissolve about 20 mg of Guaifenesin in 10 mL of Solution B.
Diluted test solution—
Transfer 1.0 mL of the Test solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dilute with Solution B to volume, and mix.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 10 µL) of the
Test solution and the
Diluted test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the areas for the major peaks. All of the peaks are baseline resolved. Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Guaifenesin taken by the formula:
F(ri / rS),
in which
F is a response factor equal to 0.63 for the guaiacol peak, having a relative retention time of 1.4, and 1.0 for all other impurities;
ri is the area of each peak, other than that of the main guaifenesin peak, obtained from the
Test solution; and
rS is the area of the main peak obtained from the
Diluted test solution: not more than 1.5% of 2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-1,3-propanediol (guaifenesin
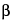
-isomer), the peak for which occurs at a relative retention time of about 0.9, is found; not more than 0.03% of guaiacol is found; not more than 0.5% of any other individual impurity is found; and not more than 1.0% of total impurities, excluding guaifenesin
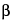
-isomer and guaiacol, is found.
Assay—
Solution A—
Prepare a mixture of water and glacial acetic acid (990:10).
Solution B—
Use acetonitrile.
Mobile phase—
Use variable mixtures of
Solution A and
Solution B as directed for
Chromatographic system. Make adjustments if necessary (see
System Suitability under
Chromatography  621
621
).
Standard preparation—
Prepare a solution of
USP Guaifenesin RS in
Solution B having a known concentration of about 0.5 mg per mL.
Assay preparation—
Transfer about 25 mg of Guaifenesin, accurately weighed, to a 50-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with Solution B to volume, and mix.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 276-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
Time
(minutes) |
Solution A
(%) |
Solution B
(%) |
Elution |
| 0–32 |
80®50 |
20®50 |
linear gradient |
| 32–35 |
50®80 |
50®20 |
linear gradient |
Chromatograph the
Resolution solution, and record the peak responses as directed for
Procedure: the relative retention times are about 0.9 for guaifenesin
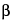
-isomer, 1.0 for guaifenesin, and 1.3 for guaiacol; and the resolution,
R, between guaifenesin and guaiacol is not less than 3. Chromatograph the
Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for
Procedure: the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 1.0%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 10 µL) of the
Standard preparation and the
Assay preparation into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the peak responses. Calculate the quantity of C
10H
14O
4 in the portion of Guaifenesin taken by the formula:
50C(rU / rS),
in which
C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of
USP Guaifenesin RS in the
Standard preparation; and
rU and
rS are the peak areas obtained from the
Assay preparation and the
Standard preparation, respectively. Calculate the percentage of C
10H
14O
4 in the portion of Guaifenesin taken. To this value, add the percentage of guaifenesin
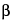
-isomer found in the test for
Chromatographic purity.