Identification—
A:
It meets the requirements of the test for Melting range.
B:
It meets the requirements of the test for Fatty acid composition.
Limit of free ethylene glycol—
Mobile phase and Chromatographic system—
Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Standard solutions—
Prepare four solutions by dissolving accurately weighed quantities of ethylene glycol in tetrahydrofuran and diluting each with tetrahydrofuran, as necessary, to obtain solutions having known concentrations of about 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, and 4.0 mg per mL.
Test solution—
Use the Assay preparation, prepared as directed in the Assay.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 40 µL) of the
Standard solutions and the
Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the ethylene glycol peaks. Plot the ethylene glycol peak responses obtained versus the concentration, in mg per mL, of ethylene glycol in the
Standard solutions. From the standard curve so obtained, determine the ethylene glycol concentration,
C, in mg per mL, in the
Test solution. Calculate the percentage of free ethylene glycol in the portion of Ethylene Glycol Stearates taken by the formula:
500(C/W),
in which
C is as obtained above; and
W is the amount, in mg, of Ethylene Glycol Stearates taken to prepare the
Test solution: not more than 5.0% of free ethylene glycol is found.
Assay—
Mobile phase:
tetrahydrofuran.
Assay preparation—
Transfer about 200 mg of Ethylene Glycol Stearates, accurately weighed, to a 5-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with tetrahydrofuran to volume, and mix.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a refractive index detector and a 7.5-mm × 60-cm column containing 5-µm 100
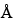
packing L21. The column and the detector temperatures are maintained at 40

.
[NOTE—Two or three 7.5-mm × 30-cm L21 columns may be used in place of the one 60-cm column provided that system suitability requirements are met; and the column temperature may be lowered to ambient temperature, although working at 40

provides stable separation conditions and ensures better sample solubility.
] The flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. Chromatograph the
Assay preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for
Procedure: the relative retention times are about 1.0 for ethylene glycol, 0.83 for monoesters, and 0.76 for diesters; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections determined from the monoesters peak is not more than 2.0%.
Procedure—
Inject about 40 µL of the
Assay preparation into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the major peaks. Calculate the percentage of free fatty acids,
E, in the portion of Ethylene Glycol Stearates taken by the formula:
IA × 270/561.1,
in which
IA is the acid value, determined in the test for
Acid value. Calculate the percentage of monoesters in the portion of Ethylene Glycol Stearates taken by the formula:
[rM /(rM + rD)](100 – D – E),
in which
rM is the peak response due to monoesters;
rD is the peak response due to diesters;
D is the percentage of free ethylene glycol in the portion of Ethylene Glycol Stearates taken, as determined in the test for
Limit of free ethylene glycol; and
E is as defined above.