DEFINITION OF TERMS
ADENOVIRUS—Virus belonging to the family Adenoviridae of DNA viruses having a nonenveloped virion with 252 capsomeres and a diameter between 70 and 90 nm; a single linear molecule of double-stranded DNA (36 to 38 kb); at least 10 structural ether-resistant and acid-stable proteins; virions are released by cell destruction.
ADENOVIRUS-ASSOCIATED VIRUS (AAV)—Human parvovirus contains a single-stranded DNA genome and depends on helper viruses (adenovirus, herpesvirus, or vaccinia-virus) for replication. Without coinfection, the wild-type virions integrate at a specific site on chromosome 19 and remain latent.
ADVENTITIOUS AGENT—A foreign substitute that is introduced accidentally or inadvertently; not natural or hereditary (as in microbial, chemical, or biochemical contamination of a purified substance).
ALLOGENEIC—From an unrelated member of the same species; from the same species, but with a different genotype.
AMPHOTROPIC VIRUS—A virus that infects and replicates in cells from multiple species.
ANCILLARY PRODUCTS—Components used during manufacturing that should not be present in the final product. Examples: growth factors, cytokines, monoclonal antibodies, cell separation devices, media, and media components.
ANTISENSE THERAPY—The use of antisense oligonucleotides (a complementary segment to RNA) to control or inhibit gene expression.
APHERESIS—Procedure of withdrawing blood from a donor, removing select components (e.g., platelets or leukocytes), and retransfusing the remainder into the donor.
AUTOLOGOUS—From one's own body.
BASE PAIR—Two nucleotide bases on different strands of the nucleic acid molecule that bond together.
BIOASSAY—Measurement of the effectiveness of a compound by its effect on animals or cells in comparison with a standard preparation. (See also Potency.)
BIOLOGICAL PRODUCT—Any virus, therapeutic serum, toxin, antitoxin, or analogous product applicable to the prevention, treatment, or cure of diseases or injuries in humans. (The term analogous product has been interpreted to include essentially all biotechnology-derived products and procedures including gene therapy, transgenics, and somatic cell therapy.)
BIOTECHNOLOGY—Any technique that uses living organisms (or parts of organisms) to make or modify products, to improve plants or animals, or to develop microorganisms for specific uses. The newer definition refers to the industrial and pharmaceutical use of rDNA, cell fusion, novel bioprocessing techniques, and gene therapy.
B LYMPHOCYTES (B cells)—A class of lymphocytes that produce antibodies and are derived from the bone marrow.
BONE MARROW CELLS—A variety of undifferentiated cells (stem cells) and differentiated cells (lymphocytes, granulocytes, erythrocytes, and platelets) found in the internal cavities of bones or bone marrow.
BONE MARROW TRANSPLANTATION—Transplantation of bone marrow cells that are capable of maintaining the hematological functions indefinitely. Technique used in the treatment of immunological disorders (severe combined immune deficiencies such as ADA deficiency), hematological disorders (anemia), metabolic disorders (Gaucher's disease), and malignant diseases (leukemia, lymphoma, or solid tumor).
CD34—Cluster of Differentiation cell-surface marker 34. CD34 is a protein that distinguishes stem and progenitor cells from more mature blood cells.
CELL LINES—Cells that are derived from primary culture embryos, tissue, or organs. Such cell lines may have a finite life span or be immortalized (made to replicate indefinitely).
CELL THERAPY—Therapy that uses whole cells to treat a disease, condition, or injury.
CGMP—Current good manufacturing practice. The FDA outlines CGMP in the 21 CFR and in the Federal Register and its Points to Consider.
CHONDROCYTES—Cells that produce the components of cartilage.
CLONAL—Genes, cells, or entire organisms derived from and genetically identical to a single common ancestor gene, cell, or organism.
CLONOGENIC ASSAY—Procedure based on the ability to give rise to a clone of cells.
COMPLEMENTARY DNA (cDNA)—DNA synthesized from an mRNA rather than a DNA template. It is used for cloning or as a DNA probe for locating specific genes.
CYTOKINE—Any factor that acts on cells; usually a protein that promotes growth.
CYTOPLASM—Cellular material that is within the cell membrane and surrounds the nucleus.
CYTOTOXIC—Able to cause cell death.
DENDRITIC CELL—Cells that sensitize T cells to antigens.
DIFFERENTIATION—A process of biochemical and structural changes by which cells become specialized in form and function.
DIPLOID CELL—A cell with two complete sets of chromosomes (see Haploid Cell).
ECOTROPIC VIRUS—A virus that infects and replicates in cells from only the original host species.
ELECTROPORATION—Physical means of gene transfer (using a brief electrical field), involving creation of temporary pores in cell membrane to introduce DNA.
ELISA—Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. An immunoassay that utilizes an enzyme-labeled antigen or antibody to detect the binding of a molecule to a solid matrix.
ENDOTHELIAL CELLS —Epithelial cells of mesodermal origin that line the internal cavities of the body, such as heart and blood and lymph vessels.
ENGRAFTMENT—Process whereby cells, tissues, or organs are implanted or transplanted into another organism. Refers both to the mechanical and the biological processes necessary to have a fully functional graft.
ENVELOPED VIRUSES—Viruses containing a lipoprotein bilayer surrounding the capsid and acquired by budding through the cell membrane of the host cells.
EPIDERMAL—Pertaining to the outermost and nonvascular layer of the skin derived from embryonic ectoderm.
EPISOMAL—Pertaining to any accessory extrachromosomal genetic material.
EPITHELIAL CELLS—Cells from the linings of various organs. Examples: respiratory, intestinal, or vascular epithelial cells.
EXTRACORPOREAL—Situated or performed outside of the body.
EX VIVO—Procedure performed outside of the living organism.
FIBROBLASTS—Connective tissue cells that have the capacity to produce collagen.
FLUORESCENCE-ACTIVATED CELL SORTER (FACS)—A machine that sorts cells based on fluorescent markers attached to them.
FORMULATED—Prepared in accordance with a prescribed method or conditions.
FUSION—Joining of the membrane of two cells, creating a daughter that contains some of the same properties from each parent cell. It is used in making hybridoma cells in which antibody-producing cells are fused to mouse myeloma cells.
G-418—The antibiotic used to select and isolate cells that contain neomycin-resistance gene.
GENE CONSTRUCT—Expression vector that contains the coding sequence of the protein and the necessary elements for its expression.
GENE THERAPY—Therapy that uses DNA to treat a disease or condition. FDA defines gene therapy products as products containing genetic material administered to modify or manipulate the expression of genetic material to alter the biological properties of living cells.
GENOME—Total hereditary material of a cell.
GERM CELL—Reproductive cell (sperm or egg), gamete, or sex cell.
GRAFT VERSUS HOST DISEASE (GVHD)—Rejection of the transplanted tissue by the host. It is the leading cause of patient death when mismatched allogeneic tissue is used.
GRAFT VERSUS LEUKEMIA (GVL)—Rejection of host leukemia cells by donor T cells.
GRANULOCYTE—One of three types of white blood cells. These cells digest bacteria and other parasites.
GRANULOCYTE–MACROPHAGE COLONY-STIMULATING FACTOR (GM-CSF)—A natural hormone that stimulates white blood cell production, particularly that of granulocytes and monocytes.
GROWTH FACTORS—Factors responsible for regulatory cell proliferation, function, and differentiation.
HAPLOID—A cell with half the usual number of chromosomes or only one chromosome set. Germ cells are haploid.
HELPER VIRUS—Aids the development of a defective virus by supplying or restoring the activity of a viral gene or by enabling the defective virus to form a functional envelope.
HEMACYTOMETER—A device used to manually count cells.
HEMATOPOIETIC—Pertaining to or affecting the formation of blood cells.
HEPATOCYTES—The predominant cell type in the liver that has an important role in metabolism and is a source of serum proteins. These cells are generally not dividing, but when injured they can divide and regenerate until the injured cells are replaced.
HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS (HSV)—A DNA virus that is a member of the family Herpesviridae. It can infect both warm- and cold-blooded vertebrates by contact between moist mucosal surfaces.
HUMAN LEUKOCYTE ANTIGEN (HLA)—Proteins controlled by the major histocompatibility complex. These proteins play a key role in determining transplant compatibility.
HUMORAL—Pertaining to elements found in body fluids (for example, humoral immunity and neutralizing antibodies).
HYBRIDIZATION DOT BLOT (DNA or RNA)—A technique for detecting, analyzing, and identifying protein; similar to the Western blot but without electrophoretic separation of proteins.
IMMUNOASSAY—Technique for identifying substances based on the use of antibodies.
IMMUNOFLUORESENCE—Technique for identifying a fluorescent label.
IMMUNOGEN—Substance capable of inducing an immune response; a form of antigen that induces immune response, as opposed to a tolerogen that induces tolerance.
IMPLANTATION VS TRANSPLANTATION—Implantation is the insertion or grafting of a biological, living, inert, or radioactive material into the body. Transplantation is the grafting of tissues from the patient's own body or from another person's body.
INSERTIONAL MUTAGENESIS—A type of mutation that is caused by the insertion of a foreign gene into a host-cell chromosome. There are multiple negative consequences of such an event, including death of a cell if an essential gene is inactivated or predisposition to cancer if a tumor suppressor gene is inactivated.
INTEGRATION—Assimilation of genetic material (DNA) into the chromosome of a recipient cell.
INTERLEUKIN (IL)—Lymphokine that regulates the growth and development of white blood cells. More than 12 have been identified.
INTRABODIES—Intracellular antibodies that are not secreted and that are designed to bind and inactivate target molecules inside cells.
IN VIVO—Procedure performed in the living organism.
IN VITRO—Procedure performed outside of the living organism. It may involve cells or tissues derived from the organisms.
ISLET CELLS—
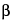
-islet cells of the pancreas that secrete insulin.
ISOGENIC—Of the same genotype.
KERATINOCYTES—Differentiated epidermal cells that constitute the top layer of cells in the skin.
LEUKEMIA—Malignant neoplasm of the blood-forming tissues.
LINEAGE (COMMITTED PROGENITOR CELLS, DIFFERENTIATED CELLS)—Specific path of cell differentiation that can be traced to a single cell of origin.
LIPOPLEX—A formulation of lipids and polymers and/or proteins.
LIPOSOME—A spherical lipid bilayer enclosing an aqueous compartment.
LYMPHOKINE—Class of soluble proteins produced by white blood cells that play a role in the immune response.
LYMPHOMA—Form of cancer that affects the lymphatic tissue.
MICROINJECTION—Physical means of gene transfer involving a direct injection of the cell with a syringe and a needle.
MACROPHAGE—Any of many forms of mononuclear phagocytes that are found in tissues and arise from hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow.
MOCK RUN—A test run that deliberately omits some critical reagents.
MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES—Antibodies that are derived from a single cell clone.
MONOCYTES—One of the three types of white blood cells. They are precursors to macrophages.
MYELOSUPPRESSION—Inhibition of bone marrow activity resulting in depletion of red cells, white cells, and platelets.
MYOCYTES—Fundamental cell units in the muscle. Target cells for insertion of genes that encode secretory proteins.
NEOMYCIN—Antibiotic derived from Streptomyces fradiae.
NAKED DNA—Isolated, purified, and uncomplexed DNA (no protein or lipid).
OLIGONUCLEOTIDE—A polymer consisting of a small number of nucleotides, usually 5 to 30.
ONCOGENES—Genes associated with neoplastic proliferation (cancer) following a mutation or perturbation in their expressions.
ONCOGENIC—Cancer-causing.
OSTEOGENIC CELLS—Derived from or involved in the growth or repair of bone.
PACKAGING CELL LINE—Cell line that produces all of the proteins required for packaging and production of viral vectors in an active form, but does not produce replication-competent virus.
p53 GENE—Gene whose mutation is the most common alteration observed in human cancers. It is not required for normal development, but the lack of this gene highly increases the potential risk of cancer.
PARVOVIRUS—DNA viruses of the family Parvoviridae. Host range includes many vertebrate species.
PERCUTANEOUS—Performed through the skin. An example of a percutaneous procedure is the injection of an agent or removal of a tissue (sample for biopsy) with a needle.
PERITONEAL MESOTHELIUM—Lining of the peritoneal cavity consisting of a single sheet of cells covering a broad surface. It has abundant lymphatic drainage and permits diffusion of macromolecules.
PLASMID—A small circular form of DNA that carries certain genes and is capable of replicating independently in a host cell.
POLYCLONAL—Derived from a population of cells consisting of many clonal types.
PROCESS VALIDATION—Means for providing documentation that the manufacturing process is controlled, reproducible, and capable of consistently producing a product that meets predetermined specifications.
PRODUCER CELL LINE—An established cell line used to produce virus vectors, often at a large scale.
POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION (PCR)—Technique to amplify a target DNA or RNA sequence of nucleotides by several hundred thousand-fold.
POTENCY—A quantitative measure of biological activity based on the attribute of the product linked to the relevant biological properties.
PROGENITOR CELL—Parent or ancestral cell, usually one that is already committed to differentiate into a specific type or lineage of cells.
PROMOTER—DNA sequence that is located at the front of a gene and controls gene expression. It is required for binding of RNA polymerase to initiate transcription.
RADIOIMMUNOASSAY (RIA)—Technique for quantifying a substance by measuring the reactivity of radioactively labeled forms of the substance.
RECOMBINANT-DNA—DNA produced by joining fragments of DNA from different sources by in vitro manipulations.
REPLICATION-COMPETENT VIRUS—A virus that can complete an entire replication cycle without a need for a helper virus; an autonomously replicating virus.
RESTRICTION ENDONUCLEASE—An endonuclease that recognizes a specific sequence of bases within double-stranded DNA.
RETROVIRUS—A virus that contains the reverse transcriptase, which converts viral RNA into DNA that then integrates into the host cell in a form called a provirus.
SERUM-FREE—Refers to cell growth medium that lacks a serum component.
SOMATIC CELLS—Cells other than the germ cells.
S PHASE—Part of the cell cycle during which DNA replication occurs.
STEM CELL—Immortal cell that is capable of proliferating and differentiating into different types of specialized cells. Each major tissue system is thought to have its own putative stem cell.
STROMAL—Refers to cellular support elements that contain essential nutrients or growth factors.
SUPRAVITAL DYE—A dye that stains only living cells.
SUSPENSION CULTURE—Cells capable of growth in suspension, not requiring substrate (attachment) on which to grow.
T CELLS—Lymphocytes that acquire functional repertoires and the concept of self in the thymus and are responsible for cell-mediated immunity. There are several subsets of T cells (helper T cells, suppressor T cells, and cytotoxic T cells).
TCID 50 ASSAY—Tissue Culture Infectious Dose, 50% Assay. An assay measuring the amount of product at which 50% of culture cells in the assay are killed (cytopathic effect) or are expressing a vector protein.
TRANSDUCTION—Transfer and expression of genetic material into a cell by means of a virus or phage vector.
TRANSFECTION—Transfer of DNA into cells by physical means such as by calcium phosphate coprecipitation.
TRANSGENE—Refers to the foreign or therapeutic DNA that is part of a vector construct.
TUMORGENICITY—Having the properties of inducing a malignant neoplasm.
VECTOR—The agent (plasmid, virus, or liposome–protein or DNA–protein complex) used to introduce DNA into a cell.
VIABILITY—State of being alive and functional.
VIRION—An elementary viral particle consisting of genetic material (nucleocapsid) and a protein covering.
VIRUS—Submicroscopic organism that contains genetic information necessary for reproduction. It is an obligate intracellular parasite.
WESTERN BLOT—An electroblotting method in which proteins are transferred from a gel to a thin, rigid support (e.g., nitrocellulose membrane) and detected by binding radioactively labeled antibody or antibody coupled to an enzyme, allowing use of a precipitating chromogenic or chemiluminescent substrate.
XENOGENEIC—From a different species.
XENOTRANSPLANTATION—Transplantation of organs from one species to another (e.g., from pigs to humans).
ZOONOSIS—The disease of animals transmitted to humans via routine exposure to or consumption of the source material.